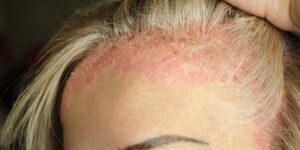
Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. It occurs when the body’s immune system sends white blood cells and other proteins to the affected area to protect it from further damage.
What is the cause of inflammation?
The cause of inflammation can be due to many factors such as physical trauma, infections, allergies, toxins, autoimmune disorders, and more.
Physical trauma can cause inflammation in the form of scrapes, cuts, sprains, and bruises. Infections such as bacteria and viruses can also cause inflammation by triggering an immune response in the body.
Allergies can also trigger an inflammatory response when a person is exposed to an allergen. Toxins like pollutants in the air or water can also lead to inflammation. In some cases, autoimmune disorders can lead to chronic inflammation where the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells instead of attacking invading pathogens. This leads to prolonged periods of inflammation that can be very damaging if left untreated.
What are the 5 classic signs of inflammation?
Inflammation is an important immune response that helps protect the body from disease and other potentially harmful invaders. The classic signs of inflammation are redness, heat, swelling, pain and loss of function.
- Redness typically occurs when there is extra blood flow to the area due to the release of chemical messengers called cytokines.
- Heat results from increased metabolic activity trying to fight off any potential threats.
- Swelling is caused by fluid leakage from capillaries as part of the inflammatory process.
- Pain typically happens when inflammation-causing substances stimulate nerve endings located around the inflamed area.
- Finally, a loss of function can occur if a joint becomes swollen or if the range of motion is limited due to pain or swelling.
Together these 5 classic signs act as early warning signals that something needs attention inside the body.
Cytokines are a type of protein released by cells to communicate with other cells. They act as signaling molecules and can help regulate the immune system and inflammatory responses. They can also be used to recruit other cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes, which then help fight infection. Cytokines can also be released in response to stress or injury, causing inflammation and activating other parts of the immune system.
Are there any home remedies for inflammation treatment?
Yes, there are many home remedies for inflammation treatment. One of the most effective is ice therapy. Apply an ice pack or cold compress on the affected area for about 20 minutes every hour to reduce any swelling, pain and stiffness.
Another effective remedy is turmeric which has anti-inflammatory properties. Try mixing a teaspoon of turmeric powder with a glass of warm milk or water and drink it twice daily. You can also try some herbal teas like chamomile, green tea, ginger or peppermint as they can help to reduce inflammation.
It’s also important to maintain a healthy diet by eating plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins to keep your body in good health. Along with these remedies, make sure to exercise regularly as physical activity can help boost your circulation and reduce inflammation. Another way to reduce inflammation is to make sure you are getting enough antioxidants, such as vitamin C, E, A, or glutathione through your diet or supplements. In addition to helping reduce inflammation, there are many potential glutathione IV benefits, such as supporting a healthy immune system.
Acute inflammation vs. Chronic inflammation
Acute inflammation and chronic inflammation are two forms of inflammation, with the former being a short-term condition while the latter is a long-term condition. The main difference between acute and chronic inflammation is the duration of the inflammatory response.
Acute inflammation typically lasts for a few hours to days and is caused by bacterial infections, tissue injury or an allergic reaction. During this period, swelling, pain and redness occur as white blood cells try to protect the area from further damage.
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent inflammation that can lead to various conditions. These include autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, type 2 diabetes, asthma and allergies. Chronic inflammation is also linked to cardiovascular diseases, cancer and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Inflammation and Arthritis
Inflammation is the body’s response to tissue damage and can be a sign of an underlying condition such as arthritis. Arthritis is a general term for conditions that involve inflammation of one or more joints, which can cause pain and stiffness in the affected area. There are many types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, and psoriatic arthritis. Treatment usually involves medications to reduce inflammation, lifestyle changes such as exercise and weight loss, and sometimes surgery.
How do I rid my body of inflammation?
Inflammation can be an uncomfortable and sometimes painful symptom of a variety of illnesses. There are several things you can do to reduce your body’s inflammation. Eating an anti-inflammatory diet, composed mainly of fresh fruits and vegetables, can help balance your body’s natural chemistry and reduce inflammation.
Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids can also be beneficial; they dissolve in the bloodstream and work to soothe swelling and calm down inflammation. It is also important to get adequate rest; fatigue can exacerbate inflammation. Lastly, de-stressing is key as stress hormones can increase levels of inflammation in the body.
Taking breaks throughout the day to practice deep breathing, light stretching, or mindfulness meditation can be helpful for managing stress levels and keeping inflammation in check.
Chronic inflammation can last for weeks, months or even years and is more often related to autoimmune diseases or prolonged exposure to certain irritants. In this case, damage to tissue occurs due to continuous stimulation of the immune system. Symptoms may include fatigue, skin changes and joint stiffness which can impair physical functioning over time.
What therapies alleviate inflammation?
Therapies that alleviate inflammation include hot and cold compresses, joint protection, and exercise. Hot compresses help to relax muscles and reduce pain, while cold compresses help to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Joint protection therapies such as splinting can also be helpful by protecting inflamed joints and providing support during activity or rest. Exercise helps to improve range of motion, circulation, strength and flexibility – all of which can help reduce pain and symptoms associated with inflammation.
Additionally, physical therapy is often recommended in order to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to one’s specific condition and needs. Medications may also be prescribed in order to control swelling, pain, stiffness and other symptoms associated with inflammation.
The goal of these treatments is to lessen discomfort caused by the inflammatory process so that individuals can return towards pre-injury activity levels as quickly as possible.
How can I prevent inflammation?
Inflammation can be both helpful in aiding the body to heal from an injury or illness, but it can also cause severe damage if left unchecked. To reduce inflammation, you should aim to make lifestyle changes such as following an anti-inflammatory diet, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight.
Additionally, reducing stress levels, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are all great ways to keep inflammation under control. Taking anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen or aspirin can also help reduce painful symptoms associated with inflammation.
If you suffer from chronic inflammation, speaking with a doctor about other medication options may be beneficial. Making small changes in your life will help prevent inflammation as well as provide many other health benefits too!
How can steroids help reduce inflammation?
Steroids are a type of medication that can be used to reduce inflammation. They work by blocking the production of substances in the body that cause inflammation. Steroids can also help to suppress the immune system, which can reduce inflammation caused by an overactive immune system.
In addition to reducing inflammation, steroids can also be used to reduce pain associated with inflammation, as well as relieve swelling and joint stiffness. Steroids should only be used when prescribed by a doctor, and should not be taken for long periods of time as they can have serious side effects. When taken properly, however, steroids can be an effective tool in reducing inflammation and its associated symptoms.